10 Business Process Examples and Best Practices Every Business Must Implement
Key takeaways
- Business process management examples demonstrate how organizations streamline workflows for efficiency and productivity.
- Companies using BPM examples have reported a 30-50% reduction in process inefficiencies.
- A strong business process model example helps businesses optimize resource allocation and reduce costs.
- Automating BPM processes leads to faster execution, reduced manual intervention, and higher accuracy.
- Tools like Cflow simplify BPM implementation, providing intuitive solutions for workflow automation and management.
Introduction
Business process management (BPM) is a systematic approach that organizations use to optimize their workflows and improve operational efficiency. BPM involves analyzing, designing, implementing, monitoring, and continuously improving business processes to enhance productivity and customer satisfaction.
Companies rely on BPM to eliminate bottlenecks, reduce manual errors, and standardize their operations for consistent outcomes. Implementing a well-defined business process model example ensures smoother execution of workflows and fosters agility in business operations. By leveraging BPM tools and strategies, organizations can adapt to changing market demands and enhance overall performance.
This blog will explore what business process management is, key statistics showcasing BPM adoption, and 10 practical examples of business process management. We will also discuss best practices for BPM implementation, the role of automation, and how Cflow serves as the ideal BPM solution for businesses.
Table of Contents
What is Business Process Management?
Business Process Management (BPM) refers to the methodology organizations use to improve and manage their business processes effectively. It involves designing workflows, identifying inefficiencies, implementing automation where necessary, and continuously monitoring progress to achieve better results.
BPM is not a one-time initiative but a continuous cycle of process optimization aimed at driving efficiency and innovation. It allows businesses to align their operational processes with strategic goals, ensuring smoother workflows and better customer outcomes.
Key aspects of BPM include:
- Process Optimization: Refining existing processes to eliminate inefficiencies and improve productivity. By identifying redundant steps, BPM ensures that businesses operate with minimal waste and maximum efficiency.
- Workflow Automation: Using technology to handle repetitive tasks, reducing the workload on employees, and increasing operational speed. Automation reduces manual interventions and enhances consistency in task execution.
- Process Analysis: Evaluating business workflows to identify areas of improvement. Companies use BPM to detect bottlenecks, track performance, and gather insights that help refine existing processes.
- Collaboration & Standardization: Aligning processes across departments for consistency. Standardized processes ensure compliance with regulations, improve interdepartmental communication, and reduce inefficiencies caused by discrepancies in workflows.
Implementing BPM ensures businesses can:
- Improve efficiency by eliminating unnecessary steps in workflows.
- Enhance agility by quickly adapting to market changes and customer needs.
- Reduce operational costs by automating processes and minimizing errors.
- Improve compliance with industry regulations and standards.
- Increase employee productivity by enabling teams to focus on high-value tasks instead of repetitive work.
By integrating BPM strategies, businesses can achieve sustainable growth and innovation. Whether it’s a small organization or a large enterprise, BPM provides the framework needed to manage operations seamlessly and drive better results.
Key Statistics on Adoption of Business Process Management
- According to McKinsey, companies implementing BPM see a 30-50% improvement in operational efficiency.
- Gartner reports that 80% of businesses will integrate BPM automation solutions by 2025.
- A study conducted by Research Nester reveals that 74% of businesses say their organization’s interest in BPM has increased, and 70% use at least one application to model processes, while 63% use one or two BPM tools to manage tasks.
- Businesses using BPM software experience a 40% improvement in compliance and governance.
10 Business Process Management Examples
Customer Onboarding Process
BPM streamlines customer onboarding by automating document verification, approvals, and account creation. Businesses use BPM to ensure that customer data is collected accurately, documents are verified seamlessly, and accounts are set up without delays. Automated workflows reduce the risk of errors and provide a smooth experience for new customers, increasing satisfaction and retention.
Invoice Processing
Automating invoice approvals and payments reduces errors and ensures faster transactions. BPM allows organizations to standardize invoice approval workflows, flag inconsistencies, and process payments in a timely manner. By integrating automation into invoice management, businesses can reduce manual intervention, improve accuracy, and maintain better financial control.
Employee Recruitment and Hiring
BPM optimizes hiring workflows, from job postings to candidate selection and onboarding. HR teams can use BPM to streamline application screening, schedule interviews, track candidate progress, and ensure compliance with hiring regulations. Automation reduces administrative burdens, enhances hiring efficiency, and improves the candidate experience.
Order Fulfillment Process
Companies enhance supply chain efficiency by automating order tracking, packaging, and dispatching. BPM ensures that orders are processed accurately and delivered on time by coordinating various stages of fulfillment. Automation helps reduce human errors, minimizes delays, and improves inventory management, leading to enhanced customer satisfaction.
IT Service Management
IT teams use BPM to manage ticketing systems and streamline issue resolutions. BPM ensures that IT support requests are categorized, assigned, and resolved efficiently, improving response times and reducing downtime. Automated workflows can escalate critical issues to the appropriate personnel, ensuring a smoother IT service experience for employees and customers.
Expense Management
BPM automation ensures better control over employee expense tracking and approvals. Organizations can set up automated approval workflows, enforce compliance with expense policies, and streamline reimbursement processes. This reduces fraudulent claims, improves financial visibility, and accelerates reimbursements for employees.
Healthcare Claims Processing
BPM helps healthcare providers streamline claims approval and reimbursement processes. Automation ensures that patient claims are verified quickly, processed accurately, and approved without unnecessary delays. This reduces administrative burdens for healthcare staff, improves patient experience, and ensures regulatory compliance.
Contract Management
Automated contract approvals and renewals ensure compliance and efficiency. BPM helps organizations manage contract lifecycles by automating document storage, tracking deadlines, and generating renewal reminders. This prevents missed contract obligations, reduces legal risks, and improves operational efficiency.
Regulatory Compliance Management
Businesses use BPM to ensure adherence to industry regulations and legal requirements. Compliance workflows help companies monitor regulatory changes, track documentation, and maintain audit trails. Automation reduces the risk of compliance violations and improves governance by ensuring all processes follow standardized procedures.
Customer Support and Ticketing
Automating customer support workflows improves response times and resolution rates. BPM ensures that customer queries are categorized, assigned to the right agents, and resolved efficiently. AI-driven automation can handle common customer inquiries, reducing agent workload and enhancing service quality.
10 Best Practices in Business Process Management
- Define Clear Objectives Establishing clear objectives before implementing BPM strategies is essential for success. Organizations should define what they aim to achieve, whether it’s improving efficiency, reducing costs, enhancing customer satisfaction, or ensuring compliance. Setting measurable goals provides direction and helps teams track progress effectively. Clear objectives also align BPM initiatives with the broader business strategy, ensuring relevance and long-term value.
- Map Out Business Processes A visual representation of workflows using BPM notation examples helps organizations understand their processes better. Process mapping allows businesses to identify redundancies, inefficiencies, and areas that need improvement. By creating detailed process maps, organizations can streamline operations, improve communication among teams, and ensure that each step contributes to the overall business objective. Proper documentation also provides a foundation for process standardization and training new employees.
- Identify Bottlenecks Analyzing current workflows is critical to identifying delays, redundancies, and inefficiencies. Businesses should conduct regular process audits and gather input from employees working on the frontlines. By pinpointing problem areas, organizations can implement targeted improvements that optimize efficiency. BPM tools provide insights into workflow performance, helping businesses detect and resolve bottlenecks proactively.
- Leverage Automation Automation is a key driver of BPM efficiency. Implementing AI-powered workflow automation for repetitive tasks minimizes manual errors, accelerates processing times, and enhances accuracy. Businesses can automate approvals, data entry, and notifications to streamline operations. Leveraging automation not only saves time but also ensures compliance with predefined business rules, making processes more consistent and scalable.
- Ensure Stakeholder Collaboration BPM is not just a technical initiative—it requires active participation from all stakeholders, including management, employees, and IT teams. Engaging all departments in BPM planning and execution ensures that processes meet business requirements and function smoothly across different teams. Collaboration fosters transparency and improves accountability, ensuring that all stakeholders work towards common goals. Encouraging employee involvement also increases the chances of successful BPM adoption.
- Monitor and Measure Performance Implementing BPM without tracking its performance is ineffective. Organizations should define key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure success, such as process cycle time, error rates, cost savings, and customer satisfaction scores. Continuous monitoring allows businesses to assess whether BPM initiatives are delivering the expected benefits. Dashboards and analytics tools provide real-time insights, helping decision-makers make data-driven adjustments for ongoing improvement.
- Adopt Continuous Improvement Strategies BPM is an ongoing process that requires continuous refinement. Businesses should establish a culture of continuous improvement by gathering feedback, analyzing process performance, and making iterative adjustments. Lean methodologies, Six Sigma principles, and Agile BPM approaches help organizations enhance efficiency and adapt to evolving business needs. By constantly evaluating and refining processes, businesses can stay competitive and responsive to market changes.
- Ensure Compliance Regulatory requirements vary across industries, making compliance a crucial aspect of BPM. Automating compliance tracking reduces the risk of human error and ensures adherence to legal and industry-specific regulations. Businesses should incorporate compliance checkpoints within their workflows to prevent regulatory violations. Auditing trails, automated approvals, and role-based access controls contribute to stronger governance and risk management.
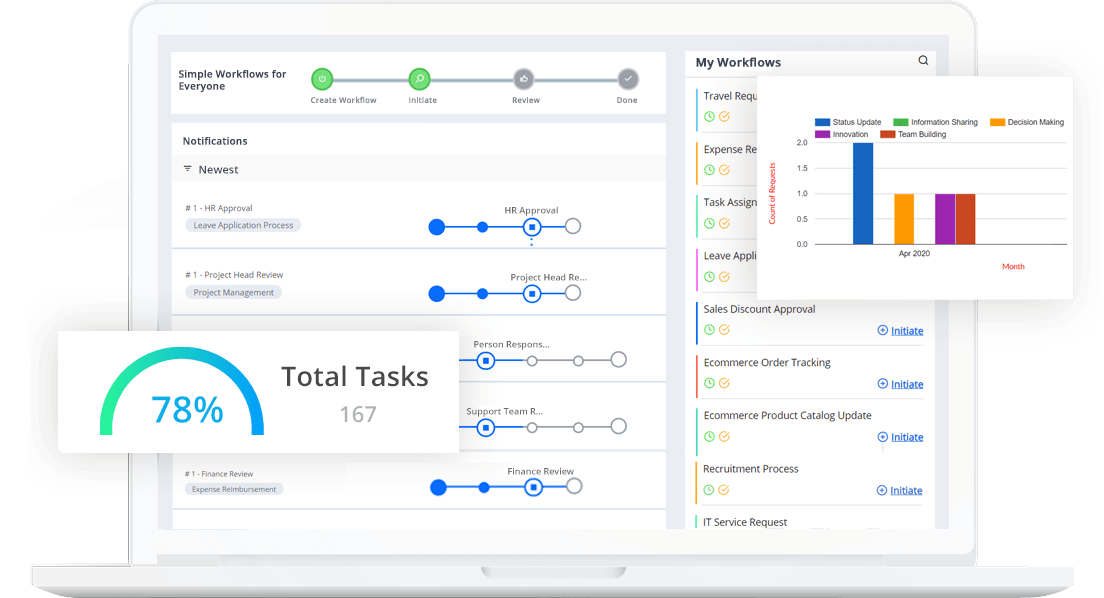
- Use BPM Software Implementing BPM manually can be challenging, especially for complex workflows. BPM software like Cflow provides a centralized platform for automating and managing business processes. These tools offer drag-and-drop workflow builders, real-time tracking, and integration with other enterprise applications. By leveraging BPM software, organizations can enhance process visibility, improve collaboration, and achieve faster execution with minimal manual intervention.
Train Employees The success of BPM depends on employee awareness and engagement. Organizations should invest in training programs to educate employees on BPM methodologies, tools, and best practices. Proper training ensures that teams understand new workflows and can effectively contribute to BPM initiatives. Continuous learning opportunities, workshops, and hands-on training sessions help employees stay updated with the latest process management techniques, fostering a culture of efficiency and innovation.
End-to-end workflow automation
Build fully-customizable, no code process workflows in a jiffy.
Automating Business Process Management – Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
- Faster Execution Automated workflows complete processes significantly faster than manual methods. By removing bottlenecks and streamlining tasks, automation reduces processing time, accelerates approvals, and ensures tasks are executed without unnecessary delays. Businesses that implement BPM automation can process orders, invoices, and service requests in real-time, enhancing overall efficiency.
- Cost Efficiency Automating business processes helps organizations reduce labor costs by eliminating redundant tasks. With BPM automation, companies can reallocate human resources to more strategic roles, reducing the need for extensive manual labor. Additionally, automation minimizes operational costs by preventing errors, decreasing rework, and optimizing resource utilization.
- Error Reduction Human errors in data entry, document processing, and manual calculations can lead to costly mistakes. BPM automation ensures accuracy by standardizing workflows and applying rule-based logic to eliminate inconsistencies. Automated validation and error-checking mechanisms further enhance data integrity, leading to better decision-making and reduced compliance risks.
- Scalability As businesses grow, manual processes can become overwhelming and unsustainable. BPM automation allows organizations to scale operations effortlessly by handling larger workloads without increasing staffing needs. Automated workflows can be customized to accommodate fluctuating demands, ensuring businesses can expand without disruptions to their processes.
- Improved Compliance Businesses operating in regulated industries must adhere to strict compliance requirements. BPM automation enforces standardized workflows, ensuring processes follow regulatory guidelines. Automated audit trails, role-based access controls, and document management systems help organizations maintain compliance, reduce the risk of violations, and prepare for audits more effectively.
Disadvantages:
- High Initial Costs Implementing BPM automation requires a substantial upfront investment in software, infrastructure, and employee training. Businesses must purchase automation tools, integrate them with existing systems, and ensure employees are adequately trained. While automation provides long-term cost savings, the initial expenses can be a challenge for small and mid-sized enterprises.
- Complex Integration BPM automation must seamlessly integrate with existing enterprise systems such as ERP, CRM, and accounting software. Integrating automation tools with legacy systems can be complex and time-consuming. Businesses may face compatibility issues, requiring additional development efforts to ensure smooth workflow integration across platforms.
- Limited Flexibility Automated processes are designed to follow predefined rules and workflows, making it difficult to adapt quickly to sudden changes. If a business experiences regulatory updates, operational shifts, or market fluctuations, modifying automated workflows may require extensive reconfiguration. This rigidity can pose challenges for industries that require high levels of flexibility.
- Security Risks Digital BPM tools handle vast amounts of sensitive business and customer data, making security a critical concern. If not properly managed, automation systems may become vulnerable to cyber threats, data breaches, and unauthorized access. Businesses must implement robust security protocols, encryption mechanisms, and access controls to protect automated workflows from potential threats.
Why Cflow is the Best Process Management Solution?
Cflow is a no-code workflow automation platform that simplifies business process management by offering a comprehensive set of tools to streamline operations and increase efficiency. Organizations across industries rely on Cflow to automate and optimize workflows, ensuring faster execution and greater accuracy.
- User-Friendly Interface Cflow provides an intuitive drag-and-drop workflow builder that allows users to create and customize workflows without any coding knowledge. Businesses can design processes in minutes, making automation accessible to all departments, including HR, finance, and IT.
- AI-Driven Automation Smart automation capabilities in Cflow reduce manual effort by learning from patterns and automating repetitive tasks. This AI-driven approach ensures that workflows remain dynamic and adapt to evolving business needs, leading to improved productivity and decision-making.
- Cloud-Based Access With cloud-based functionality, Cflow enables teams to access and manage workflows from anywhere, ensuring seamless collaboration. Remote workforces can stay connected, track tasks in real-time, and ensure business continuity without relying on physical infrastructure.
- Seamless Integrations Cflow connects with popular business tools such as Slack, Microsoft Teams, Google Workspace, and accounting platforms. These integrations enable businesses to sync data across multiple systems, reducing duplication and ensuring smooth transitions between different workflows.
- Compliance Assurance Regulatory compliance is a key focus for businesses operating in highly regulated industries. Cflow enforces compliance through built-in audit trails, automated approval workflows, and access control mechanisms, ensuring that processes adhere to industry standards.
- Customizable Workflow Automation Businesses can tailor Cflow’s automation capabilities to match their specific operational requirements. Whether managing document approvals, expense tracking, or employee onboarding, Cflow adapts to unique business needs, improving efficiency across departments.
- Real-Time Reporting and Analytics Cflow offers real-time dashboards and analytics tools that provide insights into workflow performance. Organizations can track key performance indicators (KPIs), identify bottlenecks, and make data-driven decisions to enhance efficiency.
- Scalable and Secure Designed for businesses of all sizes, Cflow ensures scalability without compromising security. Robust encryption, user authentication, and data backup mechanisms provide a secure environment for process automation.
Cflow empowers businesses to implement BPM strategies efficiently, eliminating manual inefficiencies and fostering productivity. By leveraging Cflow, organizations can enhance workflow visibility, optimize resource utilization, and drive long-term operational success.
Final Thoughts
Business process management examples showcase how organizations can enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve compliance through optimized workflows. Implementing BPM best practices ensures better control over operations and improved customer satisfaction.
Tools like Cflow simplify BPM automation, allowing businesses to streamline their processes effectively. Investing in BPM solutions ensures long-term success and agility in an ever-evolving business landscape.
FAQs
- What are some common business process management examples?
Some examples include customer onboarding, invoice processing, contract management, and IT service management. - How does BPM improve efficiency?
BPM identifies inefficiencies, automates repetitive tasks, and ensures smoother workflows. - What is a business process model example?
A business process model example illustrates workflow steps using BPM notation to visualize operations. - Why should businesses automate BPM?
Automation enhances speed, accuracy, and compliance while reducing operational costs. - What industries benefit from BPM automation?
Industries such as finance, healthcare, manufacturing, and IT benefit greatly from BPM automation. - How does Cflow enhance BPM automation?
Cflow offers AI-driven automation, seamless integrations, and cloud-based accessibility to simplify BPM implementation.
What should you do next?
Thanks for reading till the end. Here are 3 ways we can help you automate your business:

Do better workflow automation with Cflow
Create workflows with multiple steps, parallel reviewals. auto approvals, public forms, etc. to save time and cost.

Talk to a workflow expert
Get a 30-min. free consultation with our Workflow expert to optimize your daily tasks.

Get smarter with our workflow resources
Explore our workflow automation blogs, ebooks, and other resources to master workflow automation.
What would you like to do next?
Automate your workflows with our Cflow experts.